VEX REX stands for “Resource Exchange” or Decentralized Marketplace of the “network resource” in the Vexanium blockchain, REX is also a DeFi (decentralized Finance in Resource Leasing). With the REX, users of the Vexanium blockchain-based application can get resources that are at a lower cost, while the REX token holder can get passive income in the form of resource rental costs with low risk. VEX REX allows users to lease their network resources (CPU/NET) to other users for 30 days of loan requirements.
Read more: Basic Resource Tutorial – RAM, NET, and CPU on Vexanium Blockchain
Get dividends from RAM trading, account name auctions, CPU + NET rental (Premium NameBid, and CPU / NET rent / Loan). This is a Resource Exchange market created on the Vexanium blockchain that allows for free rental of bandwidth resources (CPU & NET), with the existence of this REX it solves the problem that on the blockchain platform going forward. Lenders can convert their VEX and generate stable profits while developers who need resources can borrow their VEX by paying a relatively smaller fee.
Table of Contents
How does VEX REX Works?
VEX REX provides an opportunity to earn passive income by lending (Loan) bandwidth resources (CPU + NET). This works in a very simple way that token holders lend their VEX (who are not yet in stake) or who are already stake in their respective accounts, while Dapp developers borrow their VEX to ensure they have enough resources for their application to work with smoothly without lack of resource quota. From this collaboration process, VEX holders receive additional VEX income by doing nothing and Dapp developers get almost free access to unlimited resources, this is an ideal exchange.
The VEX restriction algorithm governing resource allocation takes this into account. When a user uses resources but does not use those resources, it basically becomes an inefficient allocation of these limited resources. In short, it will make fewer resources accessible to developers and at higher costs.
REX introduces the leasing/loan market to allow VEX token holders to store their tokens for the same reason they do. This creates a free market to more efficiently allocate resources. The REX system introduces REX tokens, tokens that cannot be transferred, cannot be traded but represent claims of economic activity in the REX group, which are basically internal accounting units.
Users can get REX by lending their resources. Exchange of VEX to REX can be from VEX balances that are not already in the user’s stake, or directly from the resources of those who are already in stake, so don’t worry about unstaking before exchanging with REX. To secure the market, the purchased REX will be stored in a maturity bucket that cannot be sold until maturity (4 days after purchase).
The bucket is due in the morning at 7 am (GMT + 7). So if someone buys REX on Monday 14:00 GMT + 7, they will mature on Friday at midnight GMT + 7 around 4.4 days. The REX purchased on the following day will enter a new bucket, allowing up to 4 buckets to mature on different days.
A user can also consolidate different buckets into a new bucket which will start the new 4-day maturities process from the point of a consolidation. After the REX is due 4 days, it can be sold immediately, unless there is no liquidity or if there is not enough vex in the REX pool. Because the value of REX is relative to VEX, the value or price of REX can only go up, and it is not possible to accept a smaller amount of VEX than when they exchanged it for REX.
Therefore, REX tokens can be maintained to continuously obtain economic value from dividends in the form of VEX as a result of economic activity in the economic cycle in the REX group.
VEX REX on VEXPlorer
Now that REX is already in the Vexanium blockchain, it can be seen in a vexcore account to give a little insight into the matter of REX. Here are some terms that must be known before having REX.
- Owner: Owner of a VEX / REX Account
- Vote_stake: Number of VEX owned by the Owner
- Rex_balance: Number of REX owned by the Owner

Where does VEX REX Dividends Come From?
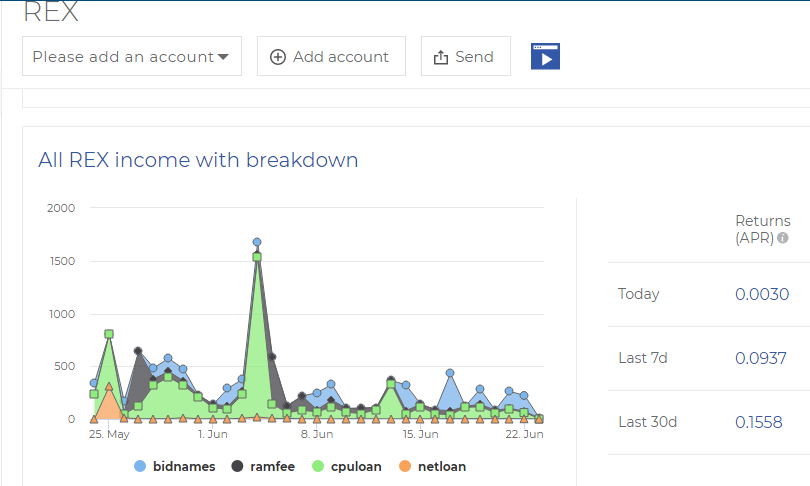
REX income sources (dividends) come from 3 items, namely:
- CPU + NET Loan
- RAM Fee
- Bid Name Fee
VEX REX Price Calculation
The price of REX is influenced by resource requests and any additional system costs that are channeled to REX.
REX Price = (Total lent VEX (Total Lend) + Total VEX completed leased (Total Unend)) / Total REX (REX Pool)
Example of REX Price Simulation (not fixed, assuming there are 100 VEX in the REX pool and 100 REX tokens):
Price REX = (0 + 100) / 100 = 1 VEX
Then the next day, the Developer takes a loan worth 100 VEX resources by paying the fee of 5 VEX tokens.
The total loan will increase by 100, the total unpaid will decrease by 100 plus the VEX 5 fee, the following calculation is obtained:
New REX price = (100 + 5) / 100 = 1.05 VEX
From the simulation above, we get a history of calculating REX prices that will never go down.
